Back pain : the disease of the century
Back pain has become one of the most common complaints in modern society. Often this pain is associated with spinal problems and leads patients to seek medical consultation.
Back pain can have several reasons; the most superficial are posture problems, especially among people who work sitting at a computer, or more profound, such as accumulated stress.
No wonder in popular parlance we say "he carries the house on his back".
Everything that impacts us in our daily life is registered in our body. Thanks to restful sleep and other sporting or artistic activities, we release a large part of our stress. But it has been observed that this is not enough.
After a few months, or even years, the body manifests itself and sends signals in the form of spinal pain.
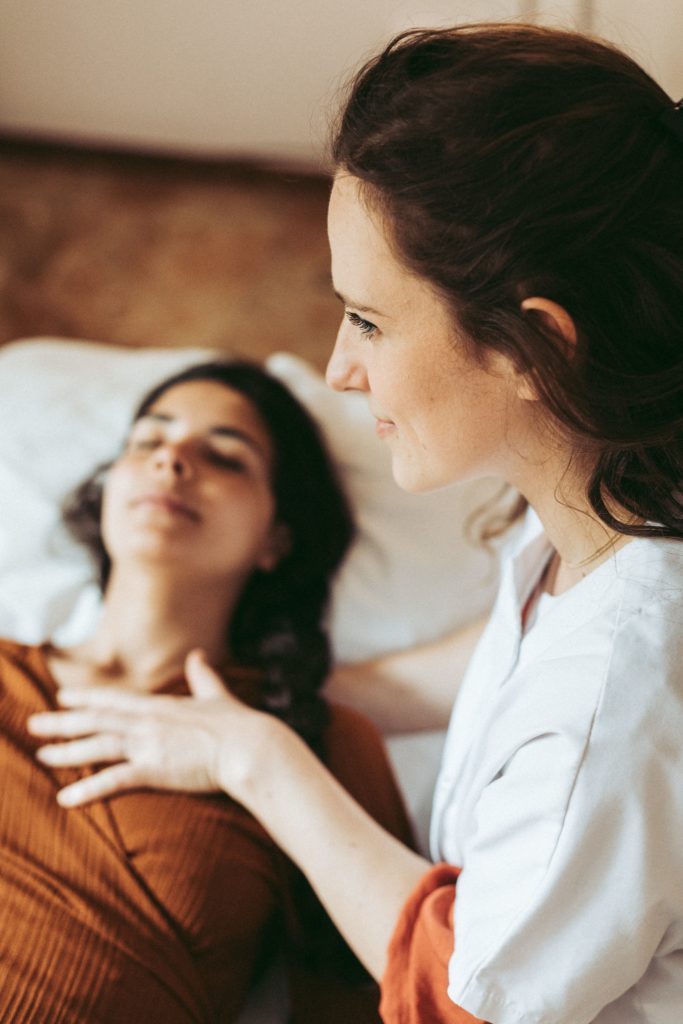
Thanks to our gentle and holistic approachwe can to bring lasting relief to our patients and also explain to them the origin of their problem so that they can, if they so wish, take action to change their habits and create new ones that favour their health.
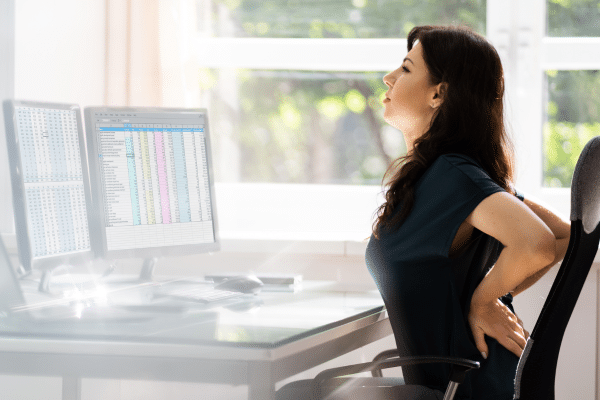

Reasons behind back pain
Superficial problems: posture
Posture plays a crucial role in the health of our spine. Incorrect posture, especially when sitting for long hours, can cause muscle imbalances, strained ligaments and pressure on the intervertebral discs.
Tips to improve posture
- Workspace adjustment: make sure your chair and desk are at a height that allows you to keep your feet on the floor and your elbows at a 90-degree angle.
- Active breaks: get up and walk or stretch every 30 minutes to avoid stiffness and promote circulation.
- Strengthening exercises: incorporates exercises to strengthen the back and abdominal core, which will help to maintain correct posture.
Profound problems: stress
Techniques to manage stress and reduce back pain
- Meditation and deep breathing: practice relaxation techniques to calm the mind and reduce muscle tension.
- Recreational activities: find hobbies or activities that you enjoy and relax, such as painting, music or gardening.
- Regular exercise: exercise releases endorphins, which are natural painkillers and improve your mood.
Appointments can be made by telephone or by WhatsApp.
The different types of back pain
Back pain is a complex and multifaceted condition that can affect people of all ages and lifestyles. Depending on its origin, pain can be classified into different types, each with its own specific characteristics and treatments.
Understanding the nature of pain is critical to effectively addressing its underlying cause and finding appropriate relief. Back pain can vary significantly in intensity, from mild discomfort to debilitating pain that affects quality of life.
In addition, the duration of pain can be temporary or chronic, persisting for months or even years. The causes of back pain are diverse, including factors such as stress, poor posture, injury, musculoskeletal disorders, and degenerative conditions.
The appropriate treatment will depend on the specific type of back pain, as well as its underlying cause. It is therefore essential to identify the type of pain in order to apply the most effective therapy.
Low back pain
Low back pain
Treatment for low back pain usually involves a combination of physical therapy, specific exercises to strengthen the muscles of the back and abdomen, and, in some cases, pain-relieving medications.
Middle back pain
Middle back pain
It can also be caused by spinal disorders such as scoliosis or degenerative disc disease. Treatment for middle back pain usually focuses on improving posture, stretching and strengthening exercises, and manual therapies such as massage or chiropractic.
Upper back pain
Upper back pain
Back pain at the level of the lungs
Back pain at the level of the lungs
Treatment may include deep breathing exercises, therapies to improve spinal mobility and relieve muscle tension, as well as management of any underlying lung-related conditions.
Back pain during pregnancy
Back pain during pregnancy
Liver and back pain
Liver and back pain
To address liver and back pain, it is essential to identify and treat the underlying cause. If you experience persistent pain in the liver and back region, accompanied by other symptoms of liver problems, it is crucial to seek medical attention for a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment.
The impact of everyday life on our health
Our body registers everything that affects us in everyday life, manifesting itself through physical signs such as back pain. Activities such as restful sleep, sport and the arts can help to relieve some of this stress, but they are often not enough. Over time, the body begins to show signs of discomfort through back pain.
Healthy habits to promote spinal health
- Balanced dietEating a diet rich in natural anti-inflammatories, such as fruits, vegetables and omega-3s, can help reduce inflammation and pain.
- HydrationDrinking enough water is essential to maintain the elasticity and health of tissues, including the intervertebral discs.
- Adequate restMake sure you get enough sleep in a position that doesn't put extra stress on your back.

Our solution: a gentle and holistic approach
Lasting pain relief
Through a gentle and holistic approach, we seek not only to relieve our patients' pain, but also to educate them about the underlying causes of their problems. This enables them, if they wish, to take steps to change their habits and adopt new behaviours that will promote their long-term health.
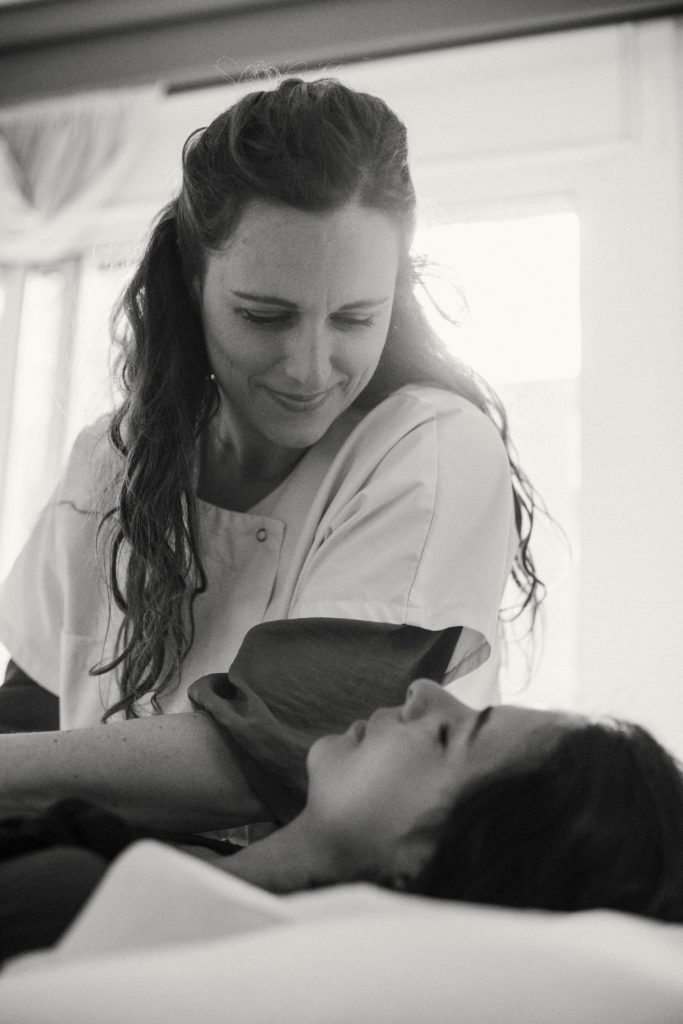
Osteopathy is a form of alternative medicine that focuses on the manipulation and movement of the muscles and skeleton to relieve pain and promote general health.
In the treatment In the treatment of back pain, osteopathy plays a crucial role due to its holistic and non-invasive approach. This section delves into how osteopathy can reduce back pain by addressing the underlying causes and promoting the patient's holistic wellbeing.
The role of osteopathy in reducing back pain
Holistic patient assessment
Osteopathic treatment begins with a thorough assessment of the patient, focusing not only on pain and symptoms, but also on lifestyle, diet and exercise habits. This comprehensive assessment allows the osteopath to understand the possible root causes of the patient's back pain, which can often be related to factors such as stress, poor posture and previous injuries.
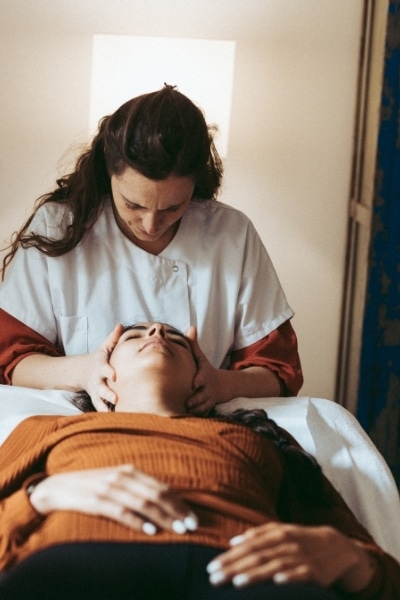
Osteopathic techniques and their benefits for back pain
Once the patient has been assessed, the osteopath employs a range of manual techniques to treat the back pain. These may include:
| Osteopathic technique | Description | Expected benefits |
| Osteopathic manipulation | Controlled movements applied to joints to improve range of motion. | Improves mobility, reduces pain. |
| Mobilisation techniques | Gentle movements to mobilise joints and soft tissues. | Restores joint function, relieves pain. |
| Muscle stretching | Application of gentle forces to stretch tight muscles and improve circulation. | Reduces muscle tension, improves circulation. |
| Deep tissue massage | Massage focused on the deeper layers of muscle and connective tissue. | Releases deep tensions, promotes relaxation. |
| Patient education | Guidance on posture, ergonomics and exercises to maintain back health. | Promotes healthy habits, prevents future injuries. |
Focus on self-healing
Education and prevention
Long-term benefits
Integration with other therapies
Osteopathy can be effectively combined with other forms of treatment, such as physiotherapy, therapeutic exercise and acupuncture, to provide a more comprehensive and personalised treatment approach to back pain.
Osteopathy offers a comprehensive and personalised approach, emphasising the importance of self-healing, prevention and patient education. By focusing on the root causes of pain and promoting holistic health, osteopathy can be a valuable tool in managing back pain and improving patients' quality of life.







Frequently asked questions about osteopathy and back pain
Nicolas and Marina answer your questions about osteopathy and back pain.



